Goal: Configure Opnsense to handle internet routing and use the L3 switch to handle Inter-VLAN routing:
In this configuration, the Opnsense VM performs firewall, packet inspection, and internet routing along with optional services like, Unbound DNS and DHCP (Kea). The L3 switch performs inter-VLAN routing between Opnsense and the VLANs. A Gateway is created in Opnsense along with static routes for returning internet packets to the correct subnets over a Transit VLAN.
Overview:
- Give the switch an IP on a subnet that will be used to configure Opnsense (ex. 10.0.0.1/30 or 29)
- Configure the LAN port on the Opnsense VM (usually done via console)
- Connect the Internet connection to the WAN port for Opnsense
- Connect the physical LAN interface from Opnsense to a physical port on the L3 switch (eth 1/2/1)
- Create a “Transit" VLAN (ex. VLAN 200) to handle routing between the L3 switch and Opnsense
- Give the Transit VLAN an IP in a subnet that will connect Opnsense
- (10.10.255.1/30 or 29)
- Give the Transit VLAN an IP in a subnet that will connect Opnsense
- Tag the Transit VLAN with the physical interface connected to the LAN port on Opnsense
- L3_SWITCH-VLAN-200 > tag eth 1/2/1
- Create the VLANs and set an IP for each virtual interface (ex. VE 20) on the L3 switch .
- Ex. 10.10.x.1 for each VLAN ## VE ##
- 10.10.50.0/24 VLAN 50 VE 50
- 10.10.60.0/24 VLAN 60 VE 60
- Ex. 10.10.x.1 for each VLAN ## VE ##
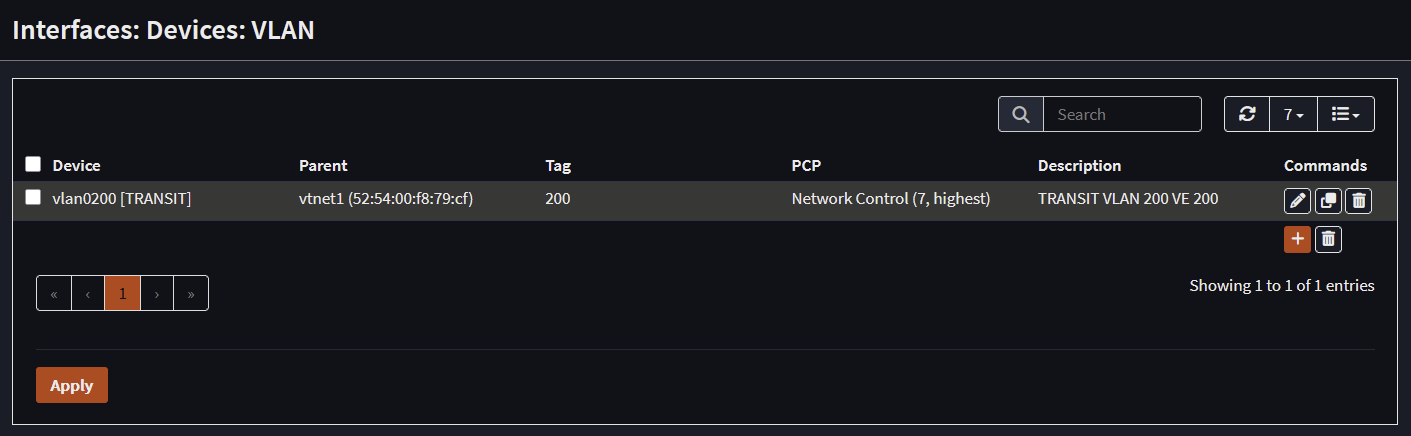
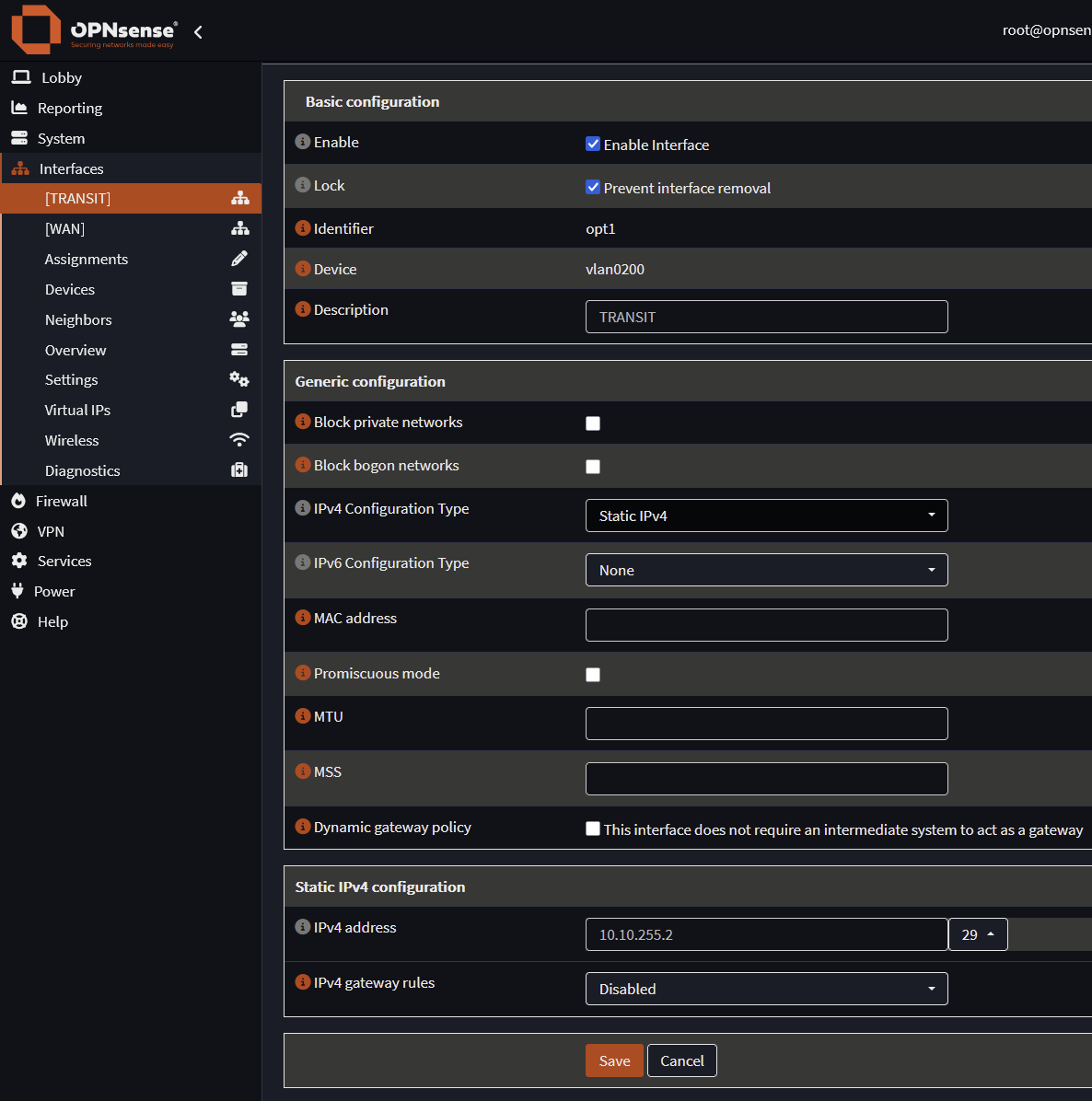
- Create an interface in Opnsense for the transit VLAN (10.10.255.2/30 or 29)
- Devices->VLAN -> Devices Assignments -> Name: TRANSIT
- Create a default route on the L3 switch pointing to the Opnsense IP on the Transit VLAN
- Ex. 0.0.0.0/0 10.10.255.2
- Test the connection and ensure you can access the switch and Opnsense Web interfaces
- UPDATE Opnsense: Log into Opensense go to System->Firmware->Updates
- Update to the latest version before configuring anything
- Set hostname, outbound DNS (ex. 1.1.1.1), and timezone: System->General
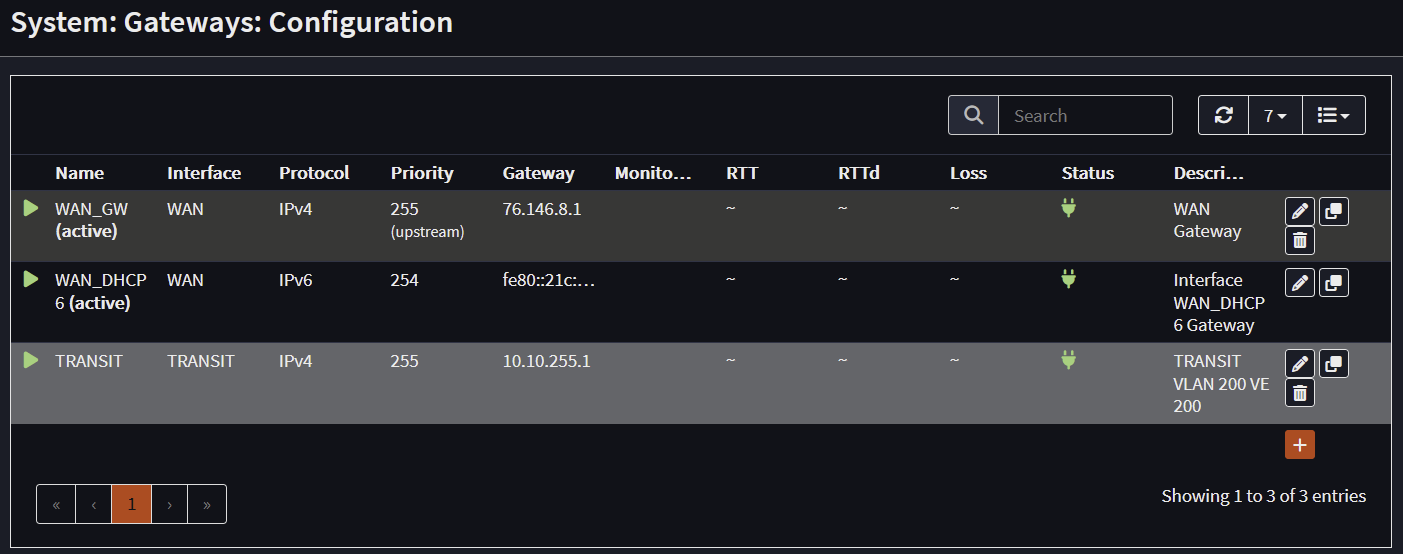
- Create a Gateway in Opnsense pointing to the L3 switch IP (10.10.255.1)
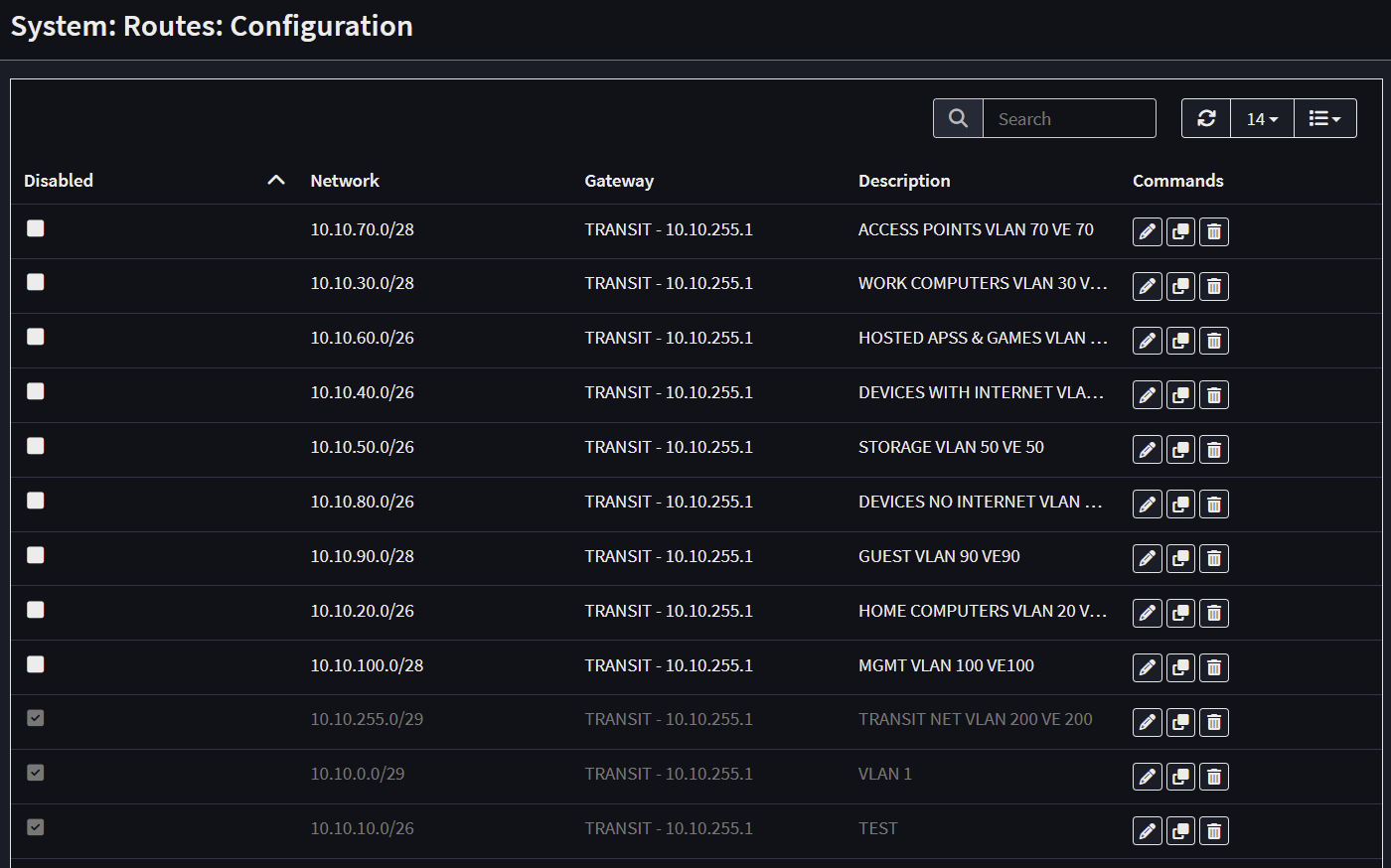
- Create Static routes Opnsense for all VLANs, point to the L3 switch Transit network's IP (ex. 10.10.255.1)
- The purpose of the static routes is to handle return traffic when hosts on the internet respond to local devices; Opnsense needs to know where to send these packets since it doesn’t have interfaces on those subnets. The IP created for the L3 switch is inside the Transit VLAN, where Opnsense does have an interface. The Transit VLAN is only for Routers & L3 switches to pass traffic between each other.
- Recommended: Disable & Delete the LAN interface(s) in Opnsense (Keep TRANSIT, WANs, VPNs, etc)
- Any firewall rules must be created in the Floating group or on the Transit Interface.
- Rule Flow: System Defined -> Floating -> Interface Groups -> Interfaces
- Use Floating rules affect all traffic to any subnet, reduces creating multiple rules
- Use the Source IP to match which device you want the rule to affect
- Inverted rules act like NOT (!) logic, use invert to block to a source or destination
- Allow Source: IOT to ! Destination: PrivateNetworks (blocks IOT from RFC1918)
- Rule Flow: System Defined -> Floating -> Interface Groups -> Interfaces
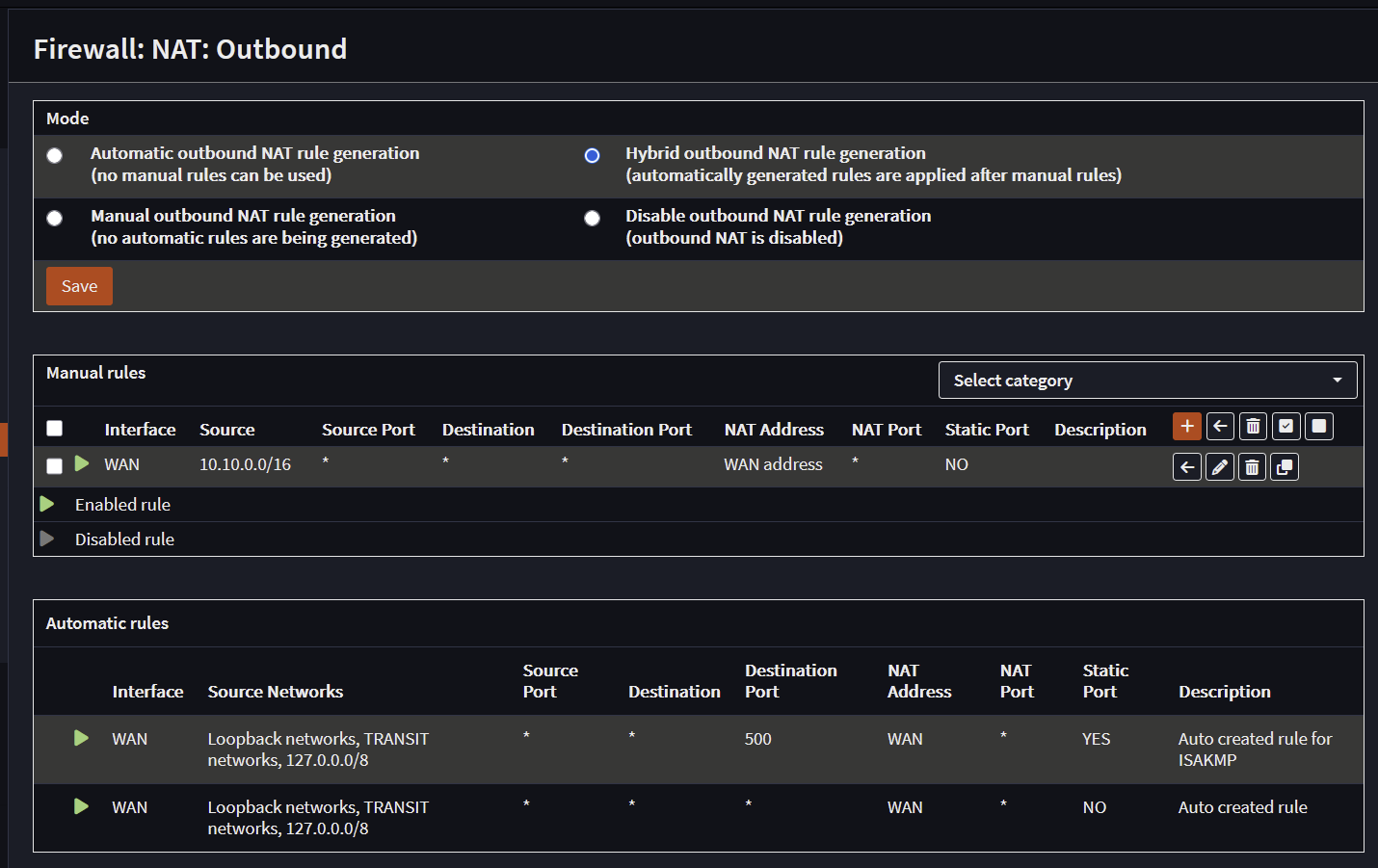
- NAT Rules need to be adjusted to use the entire network range (ex. 10.10.0.0/16) or subnets in the range.
- Enable Unbound DNS (if needed) and assign it to the Transit interface
- Use the DHCP helper feature in the L3 switch to send DHCP requests to a subnet-aware DHCP server.
- L3_SWITCH-INT-VE-50# > ip helper-address 1 10.10.255.2 = (Opnsense Kea, Win DHCP, etc.)
- L3_SWITCH-INT-VE-50# > ip helper-address 1 10.10.255.2 = (Opnsense Kea, Win DHCP, etc.)
L3 Switch Configuration
Virtual Interfaces (VE):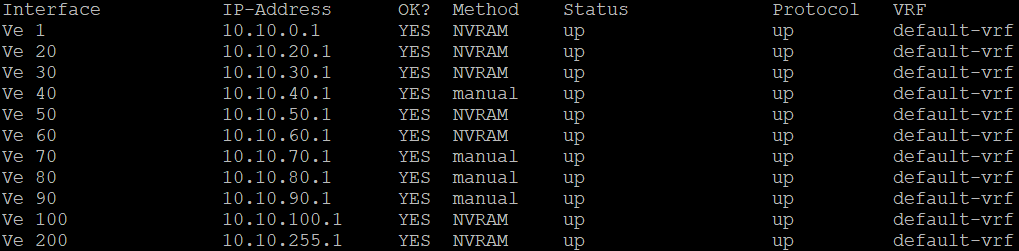 L3 Switch Route Table:
L3 Switch Route Table: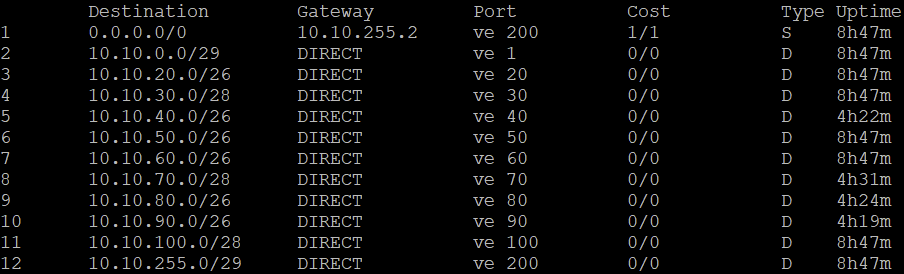
VLAN Examples:
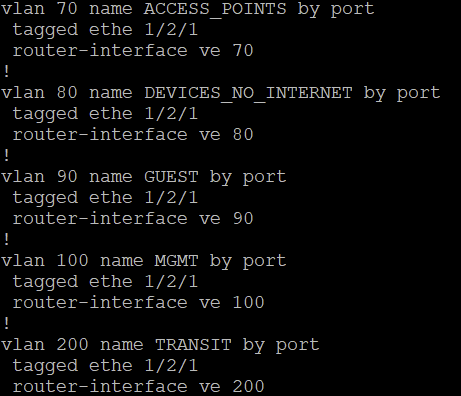
- eth 1/2/1 is tagged to all VLANs to carry them to Opnsense
- PORT-VLAN 20, Name HOME_COMPUTERS, Priority level0, Off
- Untagged Ports: (U1/M2) 3
- Tagged Ports: (U1/M2) 1
Opensense Configuration
Transit VLAN
Gateway Configuration
Uses Transit VLAN L3 Switch IP address (ex. 10.10.255.1)
Static Routes
Firewall Rules
Basic rules for Gateways and VPNs will work, but ACLs to block intra-subnet traffic must be created on the L3 switch. This is the major trade off when using this configuration, but you get the full speed of the ASIC backplane on the L3 switch. This also eliminates possible asymmetric routing issues.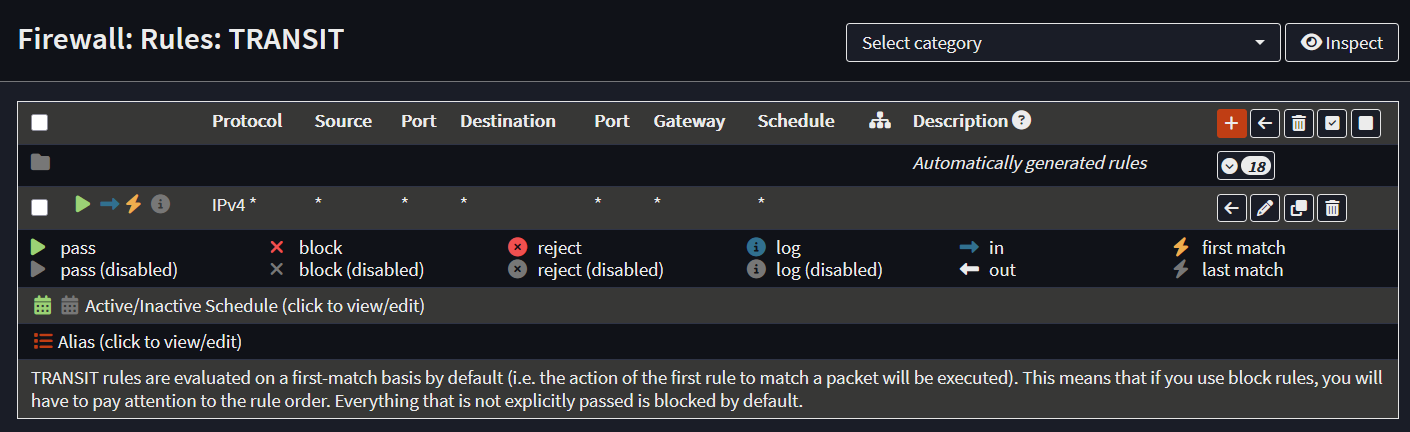
NAT Rules
Add a NAT rule for the internal network (10.10.0.0/16) and restart DHCP Kea then UnboundDNS service
Optional: Not needed in most cases: Add a static route to direct all traffic (0.0.0.0/0) to the WAN interface
Interfaces and Devices
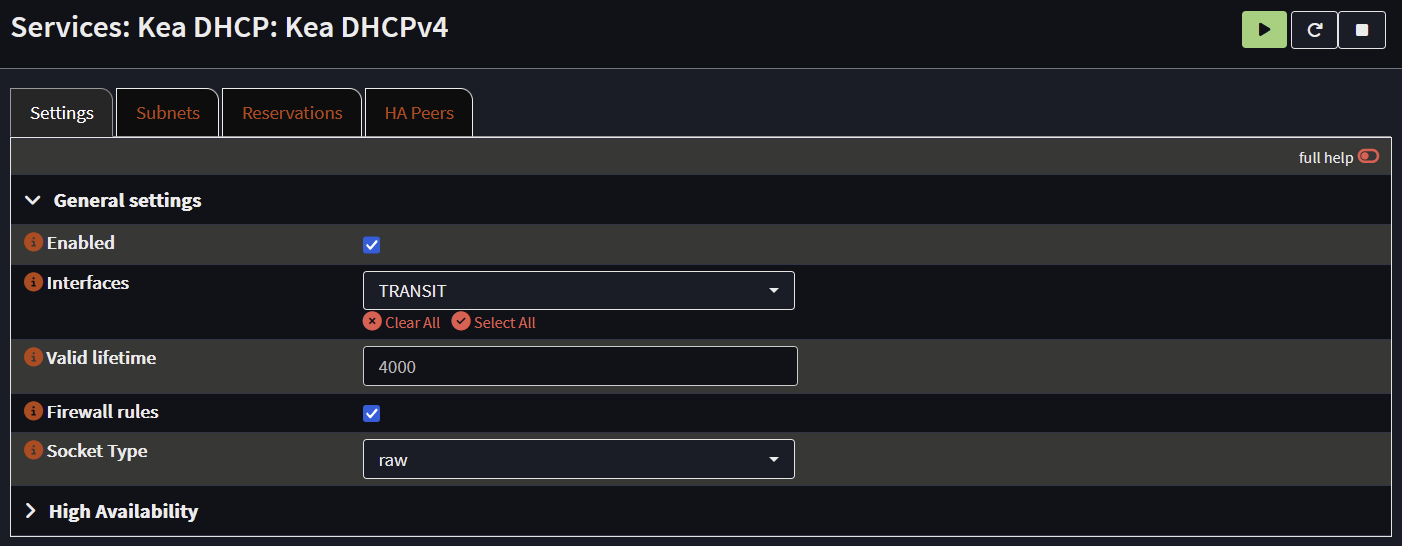
Kea DHCP
Enable Kea DHCP, set the interface to the Transit VLAN. Kea it will bind to the IP address on the Transit VLAN (ex. 10.10.255.2)
Add the IP to the helper addresses on the L3 switch VLANs (ex. ip helper-address 1 10.10.255.2)
Create Subnets set the subnet address, IP pool, gateway and DNS server.
NOTE: You must UNCHECK “Auto collect option data” to see all DHCP options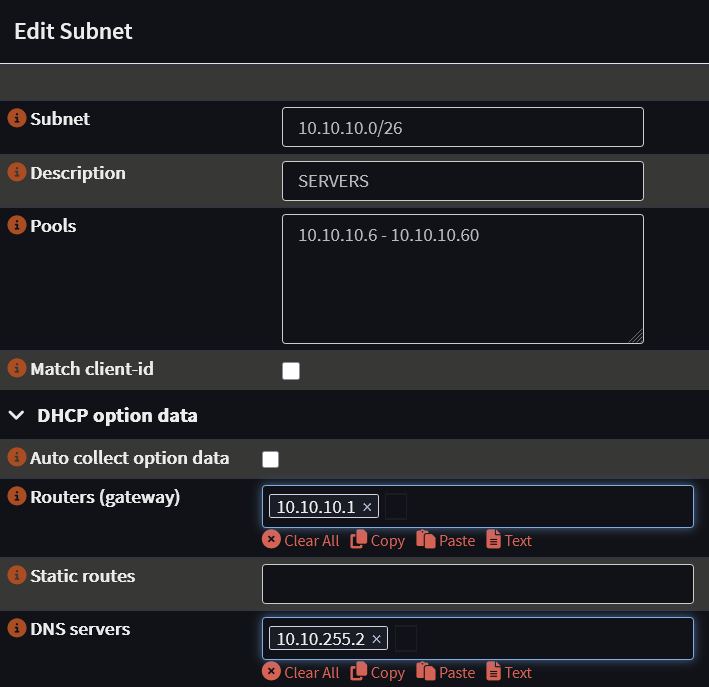
Unbound DNS
Enable Unbound and set the network interface to the Transit interface
Optional: Check Register DHCP Static Mappings to have Unbound use ISC or Kea DHCP information.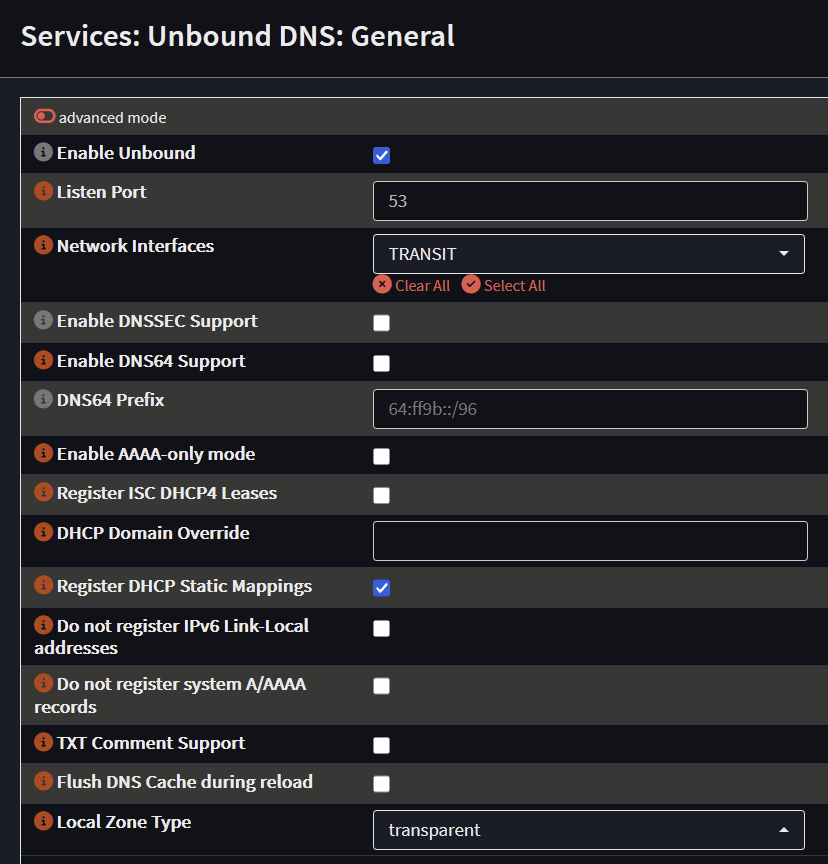
Links/References
Original post using pfsense: https://forums.servethehome.com/index.php?threads/noob-question-on-l3-switch-routing.39875/post-374782

Comments